What Is The Difference Between LED and Photovoltaic?
In today’s world, we hear a lot about both LED technology and photovoltaic systems, especially as we shift towards more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions. But what exactly is the difference between LED and photovoltaic technologies, and how do they impact our daily lives?
While both technologies play crucial roles in energy conservation and sustainability, they serve completely different functions. LED technology is primarily associated with lighting, whereas photovoltaic (PV) technology is associated with solar energy production. Although both contribute to energy efficiency, they operate in entirely different ways.

LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, which is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, which produce light by heating a filament, LEDs create light through the movement of electrons in a semiconductor material. The energy efficiency of LEDs comes from their ability to produce light without generating excessive heat.
LEDs are one of the most energy-efficient lighting technologies available today, consuming up to 85% less energy than incandescent lights. Their long lifespan and lower energy consumption make them a popular choice for both residential and commercial applications.
Applications of LEDs
LED technology is used in a wide variety of applications, from home lighting to electronic displays and automotive lighting. Here are some common uses:
- Home and Commercial Lighting: From ceiling lights to bulbs in lamps, LEDs are used to provide efficient and bright lighting in homes, offices, and public spaces.
- Displays and Screens: Many televisions, computer monitors, and digital billboards rely on LED screens for their bright and clear display capabilities.
- Automotive Lighting: Modern vehicles often use LEDs in their headlights, brake lights, and interior lighting due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
- Street Lighting: LEDs have replaced traditional street lights in many cities because they last longer and consume significantly less power.
Why are LEDs Energy Efficient?
The energy efficiency of LEDs can be attributed to their method of light generation. When electricity flows through an LED, it excites the semiconductor material, causing it to emit light directly. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which generate a lot of heat (about 90% of the energy is wasted as heat), LEDs convert most of the electrical energy into light.
Here are a few facts about LED energy efficiency:
- Long lifespan: LEDs last 25 to 30 times longer than incandescent bulbs and 3 to 5 times longer than compact fluorescents (CFLs).
- Lower energy consumption: An LED light bulb uses about 75% less energy than a traditional incandescent bulb to produce the same amount of light.
- Instant lighting: LEDs don’t require a warm-up time like CFLs, making them more efficient for tasks that need immediate illumination.
The Environmental Benefits of LEDs
LEDs are a great option for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. Their high energy efficiency and long lifespan mean fewer replacements are needed, which helps reduce the overall waste in landfills. In fact, LEDs produce nearly no UV emissions, making them a safer option for both the environment and human health.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: By consuming less electricity, LEDs help reduce the need for electricity generation, which in turn decreases the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere.
- Recyclability: Many LED components are recyclable, contributing to less e-waste compared to traditional light bulbs.
Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology
What is Photovoltaic Technology?
Photovoltaic (PV) technology refers to the process of converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels made up of photovoltaic cells. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This current is then harnessed as usable electricity.
PV systems can vary in size, from small rooftop solar panels to massive solar farms that provide electricity to the grid. As solar energy is abundant and renewable, photovoltaics play a critical role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and combating climate change.
Applications of Photovoltaic Technology
The primary application of photovoltaic technology is to generate electricity from sunlight. However, solar panels have a variety of applications depending on the installation:
- Residential Solar Systems: Homeowners install solar panels on their rooftops to generate electricity, often reducing their reliance on the grid and lowering utility bills.
- Commercial Solar Installations: Businesses install larger systems on rooftops or land to generate clean electricity, which can be used on-site or sold back to the grid.
- Solar Farms: Large-scale solar farms with thousands of solar panels are used to produce renewable energy for the national grid.
- Portable Solar Devices: Small, portable solar panels can be used to charge devices like phones, laptops, or even small appliances.
Why are Photovoltaics Important for Sustainability?
Photovoltaic technology is considered a key solution for combating climate change and reducing the carbon footprint. Unlike traditional power sources like coal or natural gas, solar power is clean and renewable, meaning it does not produce harmful emissions during its operation.
Some of the main sustainability benefits of photovoltaics include:
- Reduction in greenhouse gases: Solar energy produces no air pollution or greenhouse gases during its generation.
- Low environmental impact: After the initial environmental impact of manufacturing and installation, solar panels have a relatively low environmental footprint.
- Renewable energy: As sunlight is an inexhaustible resource, solar energy is renewable and will be available for generations to come.
The Growing Role of Solar Energy
The adoption of photovoltaic technology is rapidly increasing worldwide, as solar energy has become one of the most cost-effective sources of renewable energy. In many regions, the cost of solar panels has dropped significantly, making them accessible to homeowners and businesses alike.
Global solar power capacity has increased exponentially over the last two decades, with China, the United States, and India leading the way in solar energy generation. In addition, many governments offer incentives, rebates, and tax credits to encourage the installation of solar panels, further boosting their adoption.
Key Differences Between LED and Photovoltaic Technologies
Function and Purpose
The most fundamental difference between LED and photovoltaic technologies is their function. LED technology is designed to produce light from electrical energy, whereas photovoltaic technology is designed to generate electricity from sunlight.
- LEDs: Convert electrical energy into light, which is used for illumination in homes, offices, streets, and electronic devices.
- Photovoltaics: Convert sunlight into electrical energy, which can be used for various applications, from powering homes to charging devices.
Energy Flow and Conversion
- LEDs: The energy conversion process in LEDs involves converting electrical current into light. This process is highly efficient and produces little waste heat.
- Photovoltaics: The process of converting sunlight into electricity involves the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight excites electrons in a semiconductor material to generate an electric current.
Energy Efficiency
- LEDs: LEDs are incredibly energy-efficient, using a fraction of the energy compared to incandescent bulbs. They can produce the same amount of light while consuming only a small portion of the power.
- Photovoltaics: The efficiency of photovoltaic cells is much lower compared to LEDs in terms of energy conversion. A typical photovoltaic system may have an efficiency rate of around 15-20% (i.e., only 15-20% of sunlight is converted into usable electricity). However, advancements in solar panel technology continue to improve this efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance
- LEDs: Installation of LED bulbs is straightforward and can be done by simply replacing old bulbs. They require minimal maintenance, lasting many years before needing a replacement.
- Photovoltaics: Installation of photovoltaic systems is more complex, as it requires professional installation of solar panels, inverters, and wiring. Maintenance is minimal, but the panels should be cleaned regularly, and some components may need to be replaced after 20-30 years.
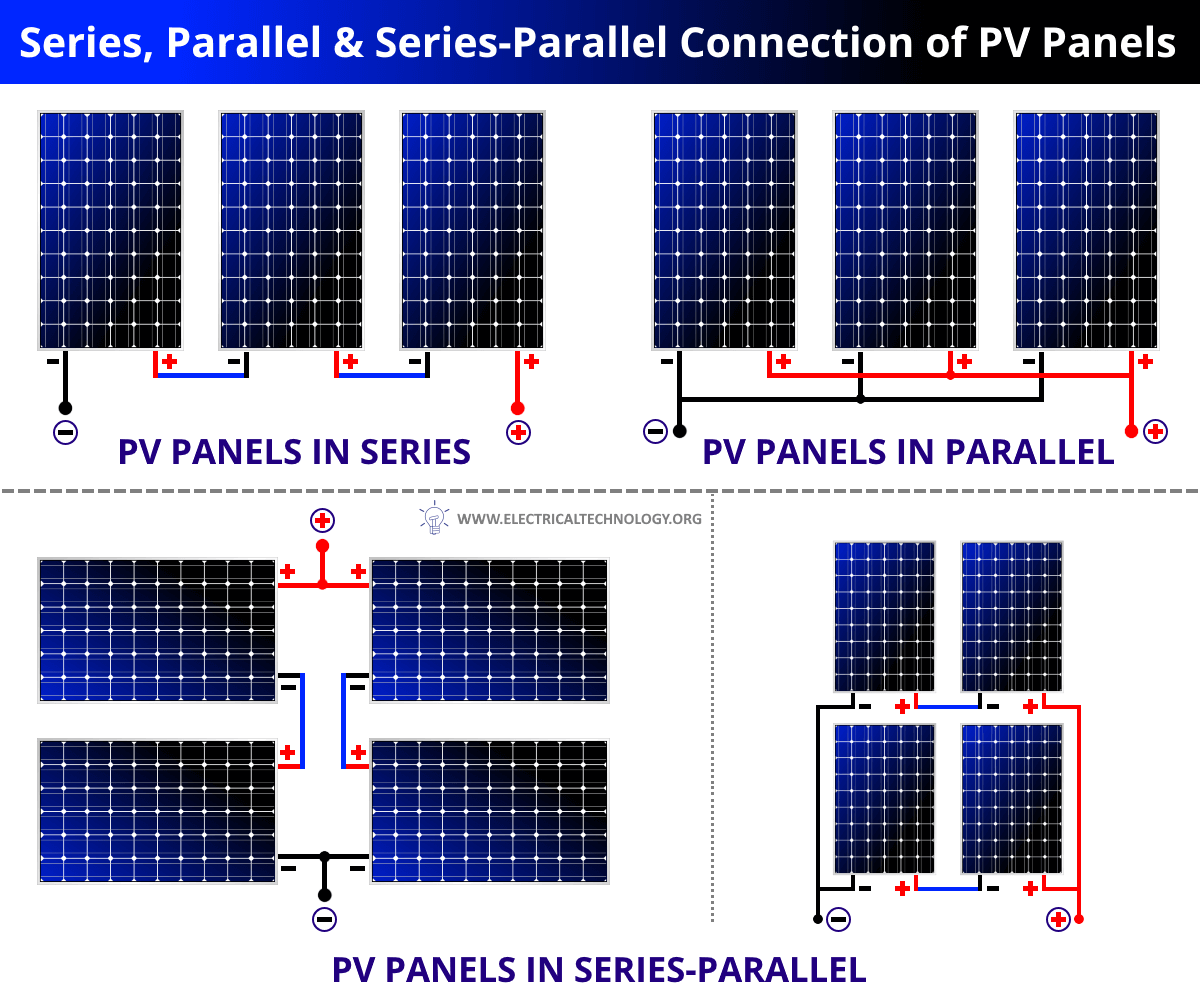
How Do LEDs and Photovoltaics Relate to Each Other?
While LED and photovoltaic technologies serve different purposes—LEDs for lighting and photovoltaics for generating electricity—these two technologies can work together in several ways to promote energy efficiency and sustainability.
Role in the Energy Ecosystem
LEDs and photovoltaics often complement each other in systems that aim to reduce energy consumption and reliance on non-renewable resources. While LED lights can significantly lower energy use for lighting, photovoltaic systems provide the renewable electricity that can power these energy-efficient lights, creating a synergistic relationship.
For example:
- Off-grid solar lighting: Many remote areas or rural communities that lack access to the electrical grid use solar-powered LED lights. These systems combine photovoltaic panels with LED lights, providing lighting without the need for traditional grid-based power.
- Solar street lights: Cities and municipalities are increasingly adopting solar-powered streetlights. These lights combine solar panels (photovoltaics) to charge batteries during the day and use LED lights for illumination during the night, ensuring an eco-friendly, cost-effective solution for street lighting.
By harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity and using energy-efficient LED lighting, these technologies help reduce overall electricity demand and cut down on carbon emissions.
Use in Solar-Powered Lighting
One of the most common ways LEDs and photovoltaic systems are combined is in solar-powered lighting applications. Whether it’s for garden lights, pathway lights, or streetlights, the combination of solar panels and LED lights offers significant benefits:
- Energy independence: Solar-powered LED lights don’t require any grid electricity, making them ideal for areas with unreliable or no access to the electrical grid.
- Low maintenance: Solar-powered LED lights require little upkeep since solar panels are durable and LEDs last for many years. This makes them a cost-effective long-term solution.
- Environmentally friendly: Solar-powered LED lights reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower electricity consumption, and have a much smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional lighting.
Pros and Cons of LED and Photovoltaic Technologies
Pros of LED Technology
LED technology is widely celebrated for its energy efficiency, longevity, and environmental benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Long lifespan: LED bulbs can last up to 50,000 hours, compared to about 1,000 hours for incandescent bulbs and 8,000 hours for compact fluorescent lights (CFLs).
- Energy-efficient: LEDs use 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs, helping to lower electricity bills and reduce energy demand.
- Eco-friendly: LEDs are free from toxic materials like mercury, making them safer to dispose of and less harmful to the environment.
- Instant lighting: Unlike CFLs, which need a few seconds to warm up, LEDs illuminate instantly, making them ideal for areas that require immediate lighting, such as streetlights and motion-sensing lights.
- Wide range of applications: From home lighting to large-scale commercial lighting and electronic displays, LEDs are versatile and used in various industries.
Cons of LED Technology
Despite their many benefits, LED technology does have some downsides:
- Higher initial cost: Although LED prices have dropped significantly over the years, they still typically cost more upfront compared to incandescent or CFL bulbs. However, the long-term energy savings generally offset this initial investment.
- Color rendering issues: Some lower-quality LED lights may have issues with color accuracy, producing a harsh or “cold” light that is not ideal for all environments.
- Limited compatibility: Not all LED bulbs are compatible with dimmer switches, though this issue is being addressed with new products designed for dimming.
Pros of Photovoltaic Technology
Photovoltaic technology has gained significant attention as a renewable energy source. Here are some of its key advantages:
- Renewable energy: Solar power is an infinite resource, as long as the sun shines, photovoltaic systems can generate electricity. This makes solar power a sustainable solution for the future.
- Low operating costs: After the initial investment for installation, the operating costs of solar panels are minimal. Solar power systems require little maintenance and have a long lifespan, often lasting 20 to 30 years or more.
- Reduced energy bills: Homeowners and businesses can save money on electricity bills by generating their own power with solar panels, especially when paired with energy storage systems (such as batteries).
- Environmentally friendly: Photovoltaic technology generates clean electricity with no emissions or air pollution, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Cons of Photovoltaic Technology
Despite the numerous benefits, there are some challenges associated with photovoltaic systems:
- High initial cost: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing a photovoltaic system can be substantial, although tax incentives and rebates may help offset these costs.
- Weather dependence: The efficiency of photovoltaic systems is directly tied to sunlight availability. During cloudy days or in regions with less sun, energy production may be reduced.
- Space requirements: Solar panels require a large area to be effective, whether on rooftops or on land. For residential installations, this may not be a concern, but larger solar farms require significant land area.
Which Is More Energy Efficient: LED or Photovoltaic?
LED Efficiency Explained
When we talk about energy efficiency in LEDs, we’re referring to their ability to provide more light per watt of electricity consumed. LEDs are by far the most efficient lighting technology available today:
- Energy consumption: LED bulbs consume about 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs and around 30% less than compact fluorescent lights (CFLs).
- Light output: LEDs can produce more lumens per watt compared to other light sources, meaning they can light up a room or space using far less power.
Photovoltaic Efficiency Explained
When discussing photovoltaic efficiency, we’re talking about the ability of a solar panel to convert sunlight into electricity. The efficiency of a photovoltaic system varies depending on the type of solar panel used and the conditions under which it operates:
- Average efficiency: Standard silicon-based solar panels typically have an efficiency rate of 15-20%, meaning only 15-20% of the sunlight hitting the panel is converted into usable electricity.
- High-efficiency panels: Newer technologies, such as monocrystalline and thin-film solar panels, offer slightly higher efficiencies, with some monocrystalline panels reaching up to 22-24% efficiency.
Comparison of Efficiency
While both LEDs and photovoltaic systems are energy-efficient in their respective domains, the efficiency of LEDs in converting electricity to light far exceeds the efficiency of solar panels in converting sunlight to electricity.
- LED lights are designed to minimize waste energy by converting most of the electrical input into light with minimal heat generation.
- Photovoltaic systems, on the other hand, face challenges such as weather dependence and the limitation of current technology, which means only a fraction of the sunlight is converted into usable electricity.
Choosing Between LED and Photovoltaic: Which One Do You Need?
When deciding whether to choose LED technology or photovoltaic systems, it’s important to remember that they serve different purposes. Here’s a guide to help you make the best decision based on your needs:
When to Choose LED Lighting
- For energy-efficient lighting: If you’re looking to reduce energy consumption for lighting, LEDs are the way to go. They are ideal for homes, offices, and outdoor lighting.
- For long-term cost savings: Although the initial cost of LED bulbs may be higher, the savings on electricity bills over time make them a worthwhile investment.
- For eco-friendly solutions: If you want to lower your carbon footprint and reduce waste, LEDs are a great option due to their long lifespan and energy efficiency.
When to Choose Photovoltaic Panels
- For renewable electricity generation: If you’re looking to generate your own renewable energy, particularly for homes or businesses, photovoltaic panels are an excellent choice.
- For reducing electricity bills: If you’re interested in cutting down on your electricity costs and reducing your dependence on the grid, solar panels are a smart investment.
- For sustainability goals: If you want to contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future, solar power is one of the best solutions, as it generates clean energy without producing greenhouse gas emissions.
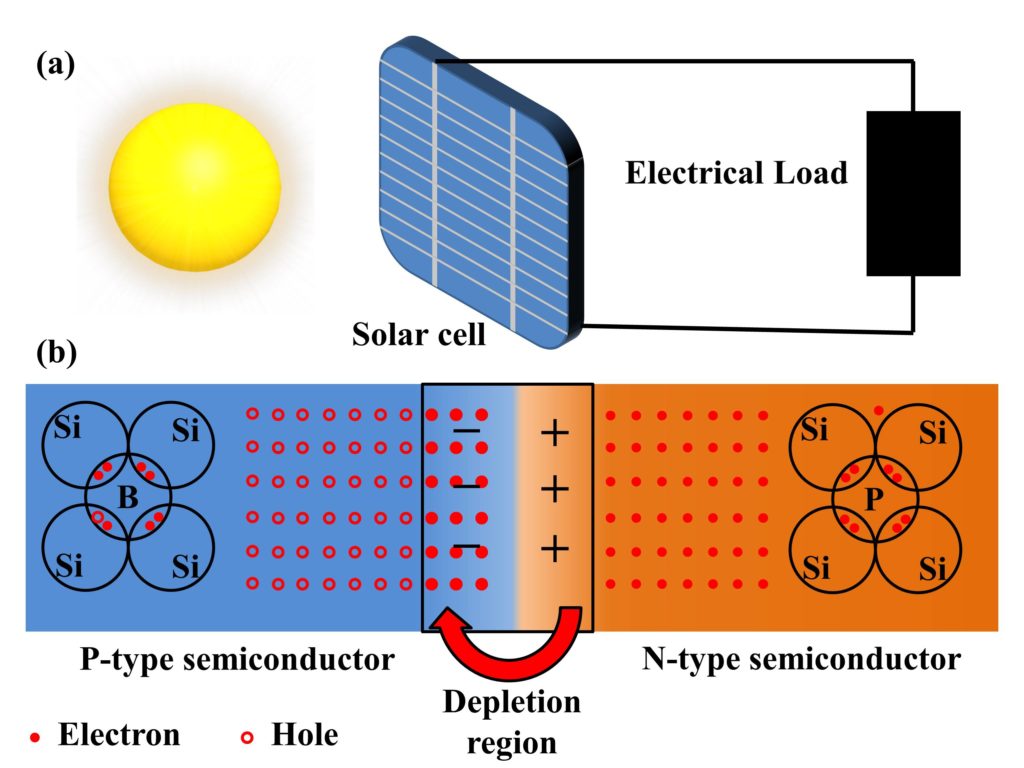
Can LED Lights Be Powered by Solar Energy?
Yes, Using Solar-Powered LED Lights
One of the most practical and energy-efficient combinations of LED and photovoltaic technology is solar-powered LED lighting. These systems use photovoltaic panels to harness the sun’s energy, which is then stored in batteries and used to power energy-efficient LED lights. These lights provide illumination without needing a direct connection to the electrical grid, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications, especially in areas where electricity access is limited or unreliable.
Solar-powered LED lights are common in street lighting, garden lights, pathway lights, and even camping lanterns. These systems are becoming increasingly popular for their eco-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and independence from the grid. Here’s how they work:
- Solar panels: The photovoltaic cells in the solar panel absorb sunlight during the day and convert it into electricity.
- Storage: The energy generated is stored in batteries (typically lithium-ion batteries), which provide power to the LEDs after sunset.
- LED lights: The stored energy powers the LED lights throughout the night, automatically turning on at dusk and off at dawn.
Benefits of Combining LED and Solar Power
The combination of LED technology and photovoltaic cells offers several advantages:
- Energy independence: Solar-powered LED lights do not rely on grid electricity, making them ideal for areas where power outages are frequent or where the electrical grid is not available.
- Cost savings: Once installed, solar-powered LED lights have minimal operating costs. They don’t require ongoing electricity purchases, which makes them a great option for reducing long-term energy bills.
- Environmental impact: Using solar energy to power LED lights eliminates the need for fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting a more sustainable future.
- Low maintenance: These systems are designed to be low-maintenance. Solar panels require little cleaning and the batteries last for several years, while LED lights can last up to 50,000 hours.
Real-world examples of solar-powered LED lights include:
- Solar streetlights in urban areas, which provide public lighting without requiring expensive electrical infrastructure.
- Solar garden lights used in residential homes to illuminate walkways and landscaping without contributing to electricity costs.
- Solar traffic signs and billboards, which use solar energy to power LED lights for greater visibility.
The Future of LED and Photovoltaic Technologies
Advancements in LED Technology
The future of LED technology looks promising, with continued advancements in both energy efficiency and functionality. Some key developments on the horizon include:
- Smart LED lighting: With the rise of smart homes, LED lights are becoming integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) technology. This allows homeowners to control lights remotely through smartphones or smart assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant. Smart LEDs are also capable of adjusting their brightness or color based on the time of day, contributing to energy savings.
- Color accuracy improvements: Ongoing developments are improving the color rendering of LEDs, allowing for a more natural light that mimics daylight and improves the ambiance of living and working spaces.
- OLEDs (Organic LEDs): A newer, more flexible version of LEDs, OLEDs offer even higher efficiency and better design possibilities for applications like televisions, computer screens, and automotive lighting. OLEDs are lighter, thinner, and capable of offering superior color quality.
- Increased energy efficiency: As LED technology evolves, we can expect even greater energy efficiency and longer lifespans. New materials and designs are being researched to improve the lumen output per watt, which will further reduce electricity consumption.
The Future of Photovoltaic Technology
Photovoltaic technology is also seeing significant advancements, particularly in the fields of efficiency, affordability, and scalability. Some exciting developments include:
- High-efficiency solar panels: Advances in materials such as perovskite solar cells and multi-junction solar cells are pushing the boundaries of solar efficiency. Perovskite solar cells, for example, have the potential to exceed 30% efficiency, which is a significant leap over traditional silicon-based panels.
- Solar rooftops and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV): We are seeing a shift towards solar rooftops and solar windows that integrate seamlessly into building designs. These BIPV systems can generate solar power while preserving aesthetics and reducing the need for large-scale solar farms.
- Energy storage integration: As the efficiency of photovoltaic systems increases, so does the need for energy storage solutions. Advances in battery technology, particularly with lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, will allow solar power to be stored more efficiently for use during cloudy days or at night, further enhancing the viability of solar energy.
- Solar-powered vehicles: The development of solar panels that can be integrated into electric vehicles (EVs) is underway. These solar-powered vehicles would be able to recharge on the go, using sunlight to supplement battery charging and extend driving range.
The Global Impact of LED and Photovoltaic Technologies
Both LED and photovoltaic technologies have a huge potential to transform global energy systems. The adoption of both technologies is growing at an accelerating rate, driven by several factors:
- Cost-effectiveness: As the technology improves and economies of scale kick in, both LEDs and photovoltaics are becoming increasingly affordable. For consumers and businesses alike, the long-term savings are substantial.
- Government incentives: Many countries are offering financial incentives, tax breaks, and subsidies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, including both photovoltaic systems and LED lighting solutions.
- Environmental policies: Governments are setting more ambitious goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability. LED and photovoltaic technologies are central to meeting these goals by cutting energy consumption and enabling cleaner energy generation.
- Rising consumer awareness: As public awareness of climate change grows, consumers are more likely to choose sustainable energy solutions. Solar power and energy-efficient lighting are some of the most accessible ways individuals can contribute to environmental conservation.
Understanding the Key Differences Between LED and Photovoltaic
While both LED and photovoltaic technologies are essential components of our transition to more energy-efficient and sustainable lifestyles, they serve different purposes and should be understood as complementary rather than interchangeable.
- LED lights are designed to save energy by providing efficient and durable illumination. They are ideal for both residential and commercial lighting, as well as in various electronic devices.
- Photovoltaic systems, on the other hand, are designed to generate electricity from the sun’s energy, offering a clean and renewable source of power that reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
The combination of these two technologies—solar-powered LED lights, for example—creates an integrated system that reduces electricity consumption, lowers energy bills, and contributes to a cleaner, greener planet. As both LED and photovoltaic technologies continue to evolve, their roles in shaping a sustainable energy future will only grow more significant.
By choosing the right technology for your needs and considering how they can work together, you can make a real difference in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability in your home, business, or community.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can LED lights work with any solar panel?
Yes, solar-powered LED lights are designed to be compatible with most standard solar panels. However, it’s essential to ensure that the wattage of the solar panel matches the energy needs of the LED light system. The panel should have enough capacity to store sufficient energy for nighttime use.
How long do LED lights last compared to photovoltaic panels?
LED lights typically last 25,000 to 50,000 hours, which is many times longer than incandescent bulbs. Photovoltaic panels, on the other hand, last 20-30 years, with a gradual decrease in efficiency over time. Both technologies have impressive lifespans, making them reliable long-term investments.
Can photovoltaic technology generate enough power to run LED lights?
Yes, photovoltaic systems can generate more than enough energy to power LED lights. Many solar-powered LED systems are designed specifically for off-grid applications, such as street lighting, garden lights, and security lighting.
What is more cost-effective: LED or photovoltaic?
In the short term, LED lights are more cost-effective since they only require an initial purchase and installation. Photovoltaic systems require a larger upfront investment for installation, but they can provide long-term savings on energy bills and even earn revenue through net metering or selling excess power back to the grid.