Solar energy has become one of the most popular and promising sources of renewable energy in recent years. As the world shifts towards more sustainable energy solutions, solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is at the forefront of this revolution. Solar PV systems are known for their ability to generate clean, eco-friendly electricity by harnessing the power of the sun. However, like any technology, solar photovoltaic energy comes with its own set of challenges.
While solar energy offers numerous benefits, it is important to understand the disadvantages of solar photovoltaic energy to make an informed decision when considering its implementation.
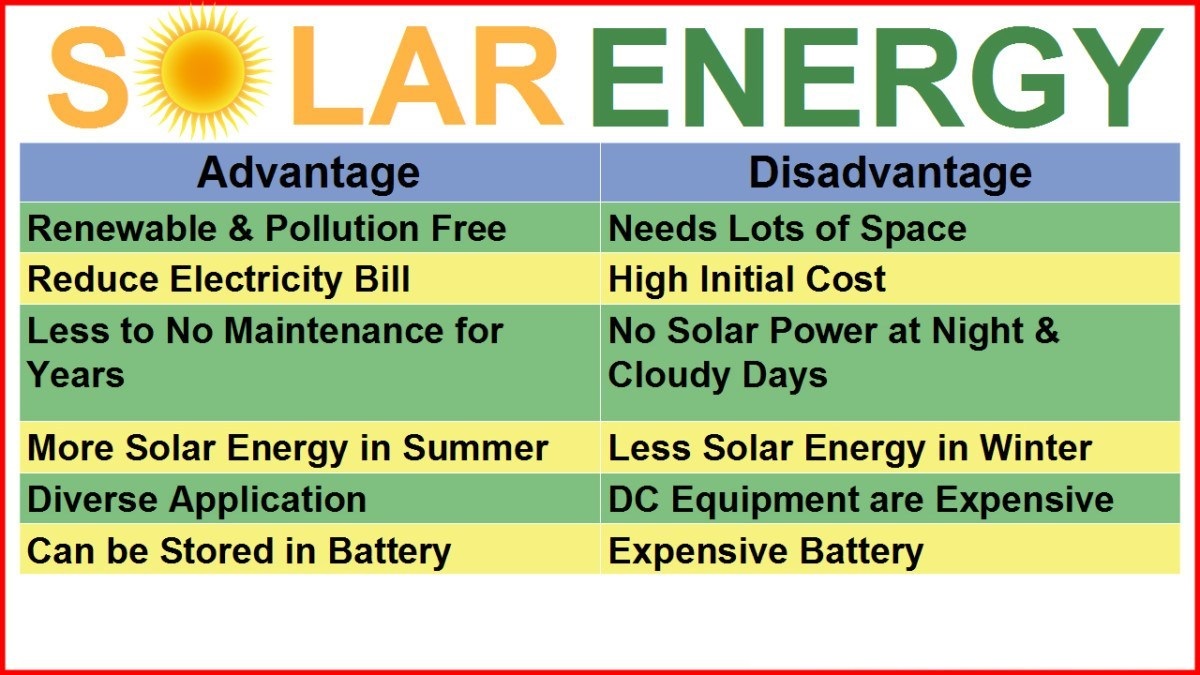
Solar photovoltaic (PV) energy is a renewable energy technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. These panels are made up of multiple solar cells, typically composed of silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight. When the photons strike the solar cells, they cause the release of electrons, creating an electric current.
There are two main types of solar PV systems:
- Residential Solar PV Systems – Installed on rooftops or properties, these systems are designed to meet the energy needs of individual homes.
- Commercial Solar PV Systems – These larger installations are used by businesses or industrial facilities to power large operations or reduce their dependence on the grid.
Solar PV systems are typically paired with an inverter that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC), which is used to power homes and businesses.
The Benefits of Solar Photovoltaic Energy
Before delving into the disadvantages, it’s essential to recognize why solar energy is so widely embraced. Here are some of the key benefits of solar photovoltaic energy:
- Environmental Benefits: Solar PV systems produce clean, renewable energy with zero emissions, helping to reduce greenhouse gases and mitigate climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power doesn’t pollute the air or contribute to environmental degradation.
- Cost Savings: Over time, solar energy can significantly reduce electricity bills. Once installed, solar PV systems generate free electricity, and many homeowners and businesses can even sell excess energy back to the grid.
- Low Maintenance: Solar panels are generally low-maintenance. With proper installation and occasional cleaning, they can last for 25 years or more, providing a long-term return on investment.
The 3 Main Disadvantages to Solar Photovoltaic Energy
While solar photovoltaic (PV) energy presents an attractive solution for reducing carbon footprints and powering homes and businesses sustainably, it is important to consider the disadvantages of solar photovoltaic energy as well. These challenges, while not insurmountable, can impact the feasibility of solar energy adoption for some users. The three main disadvantages to solar PV energy are:
- High Initial Installation Costs
- Intermittent Energy Production (Dependence on Weather and Time of Day)
- Space Requirements and Land Use
Let’s explore each of these drawbacks in more detail.
Disadvantage #1: High Initial Installation Costs
One of the biggest disadvantages of solar photovoltaic energy is the high upfront cost of installation. While the price of solar panels has dropped significantly over the past decade, the initial investment can still be a barrier for many homeowners and businesses.
Breaking Down the Costs:
The cost of a typical residential solar PV system can range anywhere from $15,000 to $30,000, depending on factors such as:
- System size (number of panels)
- Brand and efficiency of the solar panels
- Labor costs (installation)
- Permits and fees (local regulations)
For larger commercial solar PV installations, costs can reach into the hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars.
Why Is the Initial Cost So High?
The high upfront cost of solar photovoltaic energy installation includes the following:
- Solar Panels: The primary component of a PV system, which can account for about 30% to 40% of the overall cost.
- Inverter: Necessary for converting DC electricity into usable AC power.
- Installation: Professional installation is required to ensure that the system functions efficiently, which can add significant labor costs.
- Permits & Licensing: Local governments often require specific permits and inspections before installation can begin.
Can You Save Money Over Time?
Though the initial investment is high, solar photovoltaic systems can lead to substantial long-term savings. In fact, after installation, solar panels generate free electricity, significantly reducing or even eliminating monthly electricity bills. In many cases, solar users can achieve a return on investment (ROI) within 7 to 10 years.
Additionally, various financial incentives can help offset the high installation costs. These include:
- Federal Solar Tax Credit (ITC): This allows homeowners and businesses to deduct 30% of their installation costs from their federal taxes (as of 2024).
- State and Local Incentives: Many states and municipalities offer rebates, grants, and low-interest loans to make solar PV more affordable.
Despite these incentives, the high initial costs remain a significant hurdle for many potential solar adopters, especially those without the upfront capital to cover the expenses.
Disadvantage #2: Intermittent Energy Production (Dependence on Weather and Time of Day)
Another major disadvantage of solar photovoltaic energy is its intermittent nature. Unlike fossil fuel power plants that can generate electricity 24/7, solar panels are dependent on sunlight. This means that solar PV systems only produce energy during the day and their output can be dramatically affected by weather conditions.
Key Factors Affecting Solar Energy Generation:
- Daylight Hours: Solar panels generate energy during the day, with production peaking around midday when the sun is at its highest. However, during early mornings and late afternoons, solar production is lower.
- Weather Conditions: Cloudy, rainy, or snowy weather can significantly reduce the amount of sunlight that reaches the panels, decreasing the energy output. While solar panels can still generate power in cloudy conditions, they will produce much less compared to full sunlight.
- Seasonal Variations: In areas with shorter days during the winter months, solar energy generation can be reduced due to fewer daylight hours.
How Can We Overcome Intermittency?
To address the intermittent energy production challenge, several solutions are being developed:
- Energy Storage: Batteries, such as the Tesla Powerwall, are one of the most popular solutions for storing excess solar energy generated during the day. The stored energy can then be used during the night or on cloudy days. However, energy storage systems can be costly, adding to the overall expense of solar PV installations.
- Grid Connection: Many homeowners and businesses choose to remain connected to the electricity grid, which allows them to draw power from the grid during periods of low solar production. This approach is especially common in areas with unreliable weather conditions.
- Hybrid Systems: Some installations combine solar power with other renewable sources, such as wind energy, or even traditional power sources, to create a more consistent energy supply.
The Importance of Smart Grid Technology:
The integration of solar energy into the electricity grid is essential for ensuring that solar power can be distributed efficiently. Smart grids enable better energy management, allowing power from multiple sources (solar, wind, hydro) to be combined and dispatched as needed. This is key to overcoming the intermittency problem and providing a more reliable power supply.
Disadvantage #3: Space Requirements and Land Use
The space required for solar panels is another significant challenge when considering the installation of solar photovoltaic systems. For homeowners, the space requirement is typically related to the size of the roof and how much of it is suitable for panel installation. For commercial-scale projects, the land requirements can be much larger.
Space Considerations for Residential Installations:
- Roof Space: The amount of energy you can generate depends on how many panels you can install on your roof. Homes with smaller roofs or roofs with obstructions (such as chimneys or skylights) may not have enough space to install a sufficient number of panels to meet their energy needs.
- Roof Orientation: Roofs facing south (in the Northern Hemisphere) or north (in the Southern Hemisphere) tend to receive the most sunlight, while roofs with other orientations may be less efficient.
Space Considerations for Commercial and Utility-Scale Solar Farms:
For large-scale solar farms, the space requirement can be extensive. Commercial solar installations and utility-scale solar farms can require several acres of land, which is often located in rural or undeveloped areas. This can lead to challenges related to land use:
- Competition with Agriculture: In some cases, solar farms compete with agricultural land, potentially reducing space available for farming.
- Environmental Impact: Large solar farms can affect local wildlife habitats or ecosystems, depending on their location.
Solutions to Space Constraints:
To address the space requirements issue, several innovative solutions are being explored:
- Rooftop Solar: Installing solar panels on commercial rooftops or other unused building spaces can help mitigate the need for large plots of land.
- Solar Canopies: These structures use solar panels installed on elevated frameworks, providing dual use of space (such as for parking lots or walkways).
- Agrivoltaics: This practice combines solar energy production with agriculture, allowing crops to be grown underneath solar panels, making use of the same land for both food production and clean energy.

Is Solar Photovoltaic Energy Worth the Investment Despite These Disadvantages?
While the three main disadvantages to solar photovoltaic energy—high installation costs, intermittent energy production, and space requirements—are significant challenges, they are not insurmountable. As the technology and industry continue to evolve, many of these drawbacks are being mitigated, making solar energy more accessible and efficient than ever before.
Weighing the Long-Term Benefits vs. Disadvantages
Despite the initial challenges of solar PV systems, many homeowners and businesses find that the long-term benefits far outweigh the disadvantages. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Long-Term Savings
- Energy Bills: Once installed, solar PV systems produce free electricity for the life of the system. With solar panels typically lasting between 25 to 30 years, the savings on energy bills can be substantial. In fact, many homeowners and businesses see a payback period of around 7 to 10 years, after which the energy produced is virtually free.
- Rising Energy Prices: Electricity rates are rising steadily in many regions. By switching to solar power, you can hedge against future increases in energy costs. Solar energy locks in your energy costs at a predictable rate, protecting you from volatility in electricity prices.
2. Increasing Affordability and Lower Installation Costs
The cost of installing solar panels has decreased significantly over the last decade. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the cost of solar panels has dropped by more than 70% since 2010. This reduction in cost, combined with government incentives like the Federal Solar Tax Credit (ITC), makes solar energy more affordable for homeowners and businesses.
- Government Incentives: Many states offer rebates, tax incentives, and other programs to reduce the initial cost of installation. These financial incentives can significantly reduce the overall price of solar PV systems.
- Financing Options: Financing options such as solar loans, leasing, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) have made solar more accessible, allowing individuals and businesses to install solar systems with little to no upfront cost.
3. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental benefits of solar PV are profound. Solar power produces no greenhouse gases during operation, helping to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. By adopting solar energy, you are contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint: A typical residential solar system can eliminate approximately 3-4 tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually, the equivalent of planting hundreds of trees.
- Renewable Energy Source: Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to pollution, solar energy is abundant, renewable, and environmentally friendly.
Solutions and Innovations to Overcome Solar Energy’s Disadvantages
Even though solar photovoltaic energy has its disadvantages, many of these challenges are being addressed through innovation and technology. Let’s look at some of the most promising solutions.
1. Innovations in Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency of solar panels has been steadily improving, which means that panels are becoming better at converting sunlight into usable electricity. Modern solar panels can achieve efficiency rates of 18-22%, with some of the most advanced models reaching up to 25% efficiency.
- Next-Generation Solar Cells: Research is underway to develop new types of solar cells, such as perovskite and bifacial solar panels, which can capture light from both the front and back of the panel, increasing overall efficiency.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: These panels, which are made from flexible materials, are lighter and can be applied to a variety of surfaces. They are also cheaper to produce, which helps to lower the overall cost of solar installations.
2. Energy Storage and Battery Technology
Energy storage technology, such as solar batteries, is improving rapidly, helping to solve the issue of intermittent energy production. These batteries store excess energy produced during the day for use at night or on cloudy days.
- Tesla Powerwall: One of the most popular energy storage solutions, the Tesla Powerwall, allows homeowners to store up to 13.5 kWh of energy, which can power an average home for about one to two days.
- Emerging Storage Solutions: Solid-state batteries and flow batteries are promising new technologies that could significantly reduce the cost and increase the storage capacity of solar energy systems.
3. Alternative Uses of Land and Space
As mentioned earlier, land use for large solar farms can be a challenge. However, several innovative solutions are being explored to address space constraints:
- Rooftop Solar: Rooftop solar panels are one of the most efficient ways to install solar PV systems in urban environments. They utilize underutilized space on rooftops, eliminating the need for large tracts of land.
- Agrivoltaics: This practice involves growing crops beneath solar panels, allowing land to be used for both agriculture and energy production. This is a win-win for landowners and farmers, as they can generate income from both solar power and crops.
- Solar Canopies: Solar canopies are elevated solar systems that can be installed over parking lots, walkways, and other areas. These systems allow for dual use of space and protect vehicles from the elements while generating renewable energy.
4. Improved Grid Integration
The integration of solar energy into the electricity grid has been an ongoing challenge. However, smart grids and microgrids are helping to optimize the distribution of solar energy and reduce grid congestion. Smart inverters can adjust solar output to match grid demand, allowing for more stable energy production.
- Virtual Power Plants (VPPs): VPPs aggregate the output of thousands of small-scale solar systems, including residential solar panels and batteries, to create a large, distributed power plant. This allows for better coordination and more efficient energy distribution.

FAQs About Solar Photovoltaic Energy and Its Disadvantages
As we’ve discussed, solar photovoltaic energy offers both substantial benefits and challenges. To help clarify some common questions, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about solar photovoltaic energy and the disadvantages of solar PV.
Can Solar Panels Still Work on Cloudy Days?
Yes, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy or overcast days, but their efficiency will be reduced compared to sunny days. On cloudy days, solar panels might produce only 10-25% of their peak energy output, depending on the density of the clouds.
While solar panels rely on direct sunlight for maximum efficiency, they can still produce energy from diffuse sunlight that reaches Earth through the clouds. This means that even in less-than-ideal weather conditions, solar panels will continue to work—just not as efficiently.
To address this intermittency, many solar system owners combine their installations with battery storage or remain connected to the electric grid, which allows them to draw energy during periods of low solar production.
How Much Does Solar PV Installation Cost?
The cost of installing a solar photovoltaic system can vary widely based on location, system size, and the type of solar panels used. Here’s a breakdown of typical costs:
- Residential Solar Systems: The average cost of installing a solar PV system for a home typically ranges from $15,000 to $30,000, depending on the size of the system and installation requirements. This estimate includes both the panels and the inverter, as well as labor costs for installation.
- Commercial Solar Systems: Commercial-scale installations can be significantly more expensive, with costs often ranging from $100,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on the size and complexity of the system.
It’s important to note that these costs are often offset by financial incentives, such as the federal solar tax credit, state rebates, and financing options.
What Happens to Solar Panels When They Reach the End of Their Lifespan?
Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, but after that, their efficiency starts to decrease. However, even at the end of their lifespan, solar panels still generate some electricity, just at a lower rate.
When solar panels reach the end of their useful life, recycling is essential to reduce environmental impact. Modern solar panels can be recycled, and their valuable components (such as silicon, aluminum frames, and copper wiring) can be reused.
Some companies offer solar panel recycling programs, and research is being done to improve the efficiency and sustainability of solar panel recycling processes. The industry is actively working toward reducing the environmental impact of decommissioned panels.
Can I Install Solar Panels If I Don’t Have Enough Roof Space?
Yes, even if your roof doesn’t have enough space to accommodate a full solar PV system, there are still options available. Here are a few alternatives:
- Ground-Mounted Solar Panels: If you have enough land, you can install solar panels on the ground, either in your backyard or on a plot of land nearby.
- Solar Canopies: These elevated solar panel systems are installed above parking lots or other open areas, freeing up valuable roof space for other uses while still generating solar energy.
- Community Solar Programs: If your roof is unsuitable for solar panels, you can participate in community solar projects, where you buy or lease a share of a larger solar installation in your area. This allows you to benefit from solar energy without the need for individual installation.
Is Solar Energy Viable in Regions with Limited Sunlight?
While solar energy is most efficient in sunny regions, it is still viable in regions with limited sunlight. Even in cloudy or colder climates, solar panels can produce energy, although their output will be lower compared to sunnier regions.
In places with less consistent sunlight, a few strategies can improve the effectiveness of solar PV systems:
- Higher-Efficiency Panels: Choosing high-efficiency solar panels (such as monocrystalline panels) can help make the most of limited sunlight.
- Energy Storage: Installing solar batteries can help store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or on cloudy days.
- Hybrid Systems: In areas with significant variability in sunlight, combining solar PV with other renewable energy sources, like wind energy or hydroelectric power, can help ensure a consistent energy supply.
Some regions with fewer sunny days, like parts of Germany and Canada, have still been able to successfully adopt solar energy, demonstrating that solar PV is a versatile and reliable energy source, even in less-than-ideal climates.
What are the 3 main disadvantages to solar photovoltaic energy? While high installation costs, intermittent energy production, and space requirements present real challenges, these issues are being addressed through technological advancements, financial incentives, and innovative solutions.
The environmental benefits of solar PV—such as reducing carbon emissions and providing clean, renewable energy—are undeniable. Furthermore, solar energy has become more affordable in recent years, with lower installation costs, increased efficiency, and growing availability of financing options.
By investing in solar photovoltaic energy, you are not only contributing to a sustainable future but also potentially saving money in the long run. As technology continues to improve, the disadvantages of solar energy will likely diminish, making solar power an increasingly attractive option for homeowners, businesses, and governments alike.
Solar PV remains one of the most promising solutions to the world’s energy challenges, and with continued innovation, we can expect even greater progress in harnessing the power of the sun.
